Best Practices for Protecting your Product Data While Working With a Distributed Team

With the world turning increasingly digital and remote, product data leakage is becoming a real threat for many organizations.
According to the IBM/Ponemon Institute report, the overall expense of data breaches in 2022 was $4.35 million, with the violations in the healthcare sector averaging $10.10 million.
Meanwhile, breaches that occurred in the United States had the highest expenses, averaging $9.44 million.
In this article, we’ll observe the main threats to product data for an organization with distributed teams and showcase five best practices that can help protect your product data.
What is product data?
Product data refers to all the product-related information, including data about its features, technical specifications, description, images, etc. It may also include information about user preferences and demographic data used by various teams and team members, especially in marketing and sales departments, to improve customer relations and customize the user experience.
In today’s digital era, the significance of data is rising at an enormous pace. Businesses rely on this data to make informed decisions required for the successful operation of a company. As a result, protecting this data from potential data leakage or other data breach threats has become the key priority for all types of companies, from SMBs to giant corporations.
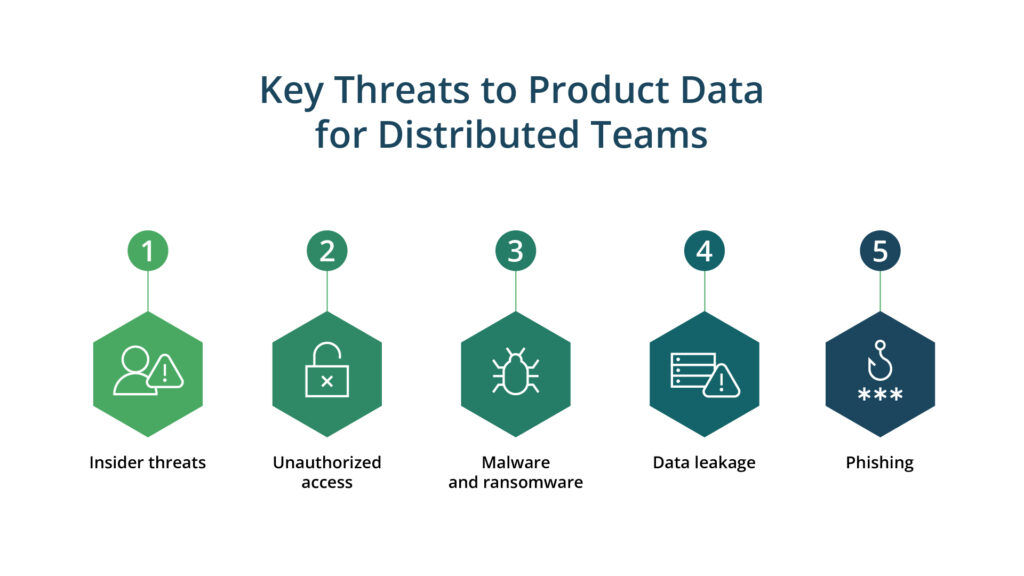
Key threats to product data while working with distributed teams
When working with distributed teams, protecting product data becomes even more challenging due to the increased risk of data breaches and cyberattacks. Here are some of the main product data threats to be aware of:
Insider threats
Insider threats occur when an employee causes intentional or unintentional harm to the company by stealing sensitive information or leaking confidential data. In distributed teams, these malicious activities can be challenging to trace and prevent since, in a remote mode, data protection practices may have weaker control than in traditional office conditions.
Unauthorized access
One of the main product data threats is unauthorized access, which can occur when someone gains access to sensitive information without permission. It can happen due to weak passwords, stolen login credentials, or unsecured communication channels. Distributed teams may also face the risk of internal threats from employees who have been granted access but abused it for their interests.
Malware and ransomware
Product data security for distributed teams can be put at risk by malware and ransomware attacks. In these attacks, malicious software infects systems, steals sensitive data, or locks users out of their systems until a ransom is paid. Distributed teams are especially vulnerable to such attacks since they work on various devices and may not have consistent security protocols in place.
Data leakage
Data leakage is another threat to product data. This issue may occur when sensitive data is intentionally or unintentionally shared or leaked through insecure channels. One example is when employees accidentally share confidential information while communicating via unencrypted email or messaging apps or store data in unsecured locations.
Phishing
Phishing is also a significant threat to product data security. It may include various tricks with the end goal of forcing employees to disclose sensitive information, such as credentials or financial data. Distributed teams are prone to falling for these tricks more often since, in a non-traditional office environment and while working on multiple devices, employees may fail to follow the security guidelines strictly.
5 best practices for protecting your data in a distributed team landscape
Below we will provide you with 5 preventive tactics that can help your organization avoid or minimize the risks associated with product data breaches.
Access control policies
Access controls imply that you should limit the number of users who have access to sensitive information and the list of actions they can take toward it. Role-based access control can help assign different levels of permissions based on the user’s position in an organization. For example, when it comes to the program’s source code, a software developer and a marketing manager will get various levels of access to it.
Security of communication
Secure communication is the basic step in protecting your product data. Email, video conferencing, and messaging apps — you need to ensure that any tool an organization uses has end-to-end encryption, i.e., guaranteeing that only the main members of communication (sender and recipient) can read the messages. Strong passwords and two-factor authentication are the other two steps to prevent unauthorized access.
Cloud-based storage
Storing your product data in the cloud is a big step forward in your data protection policy. Data encryption and firewalls are just a few tools you can use to protect your data in the cloud. Backup and disaster recovery tools will help guarantee that your data is safe during a breach or natural disaster.
Security audits
Regular audits to ensure your product data is secure is vital for a business. Security audits include reviewing your access controls, storage providers, and communication tools and timely detection of vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Within the audit, you should also test your team’s expertise in cybersecurity best practices and conduct penetration testing to reveal any potential breaches.
Team training
Finally, training your team is vital in protecting your product data. It may include various techniques, from educating your staff on how to create strong passwords, teaching them to detect phishing emails, and using secure communication tools. As a fundamental final step, you should also establish clear policies on handling sensitive information and follow guidelines on what to do during a data breach.
Conclusion
We’ve observed the main threats to product data for an organization with distributed teams and showcased five practices that can help protect your data.
Obviously, protecting your product data while working with a distributed team requires a multi-faceted approach. You will safeguard your company’s sensitive information by implementing access controls, using cloud-based storage, providing secure communication tools, and conducting regular team training on cybersecurity best practices and audits.
At Kanda, we know how to build software tailored to the organization’s security protection goals. Whether you have a traditional office environment or a distributed team scattered worldwide, you will deliver a secure, reliable, and scalable end product.
Talk to our experts to start your path to building secure software now.