
Data Security: 6 Strategies to Protect Your Business
The business value of data has never been greater. 75% of customers report they would not buy from a company they do not trust to protect their data. Last year, however, became record-breaking in terms of data breaches, showing a 68% jump from the previous year. Given a vastly expanded attack surface due to an abrupt shift to working from home and the lack of proper security protections, IT environments are a low-hanging fruit for cyber criminals. The most common reasons include compromised credentials (19%), cloud misconfigurations (19%), and vulnerability in third-party software (16%).
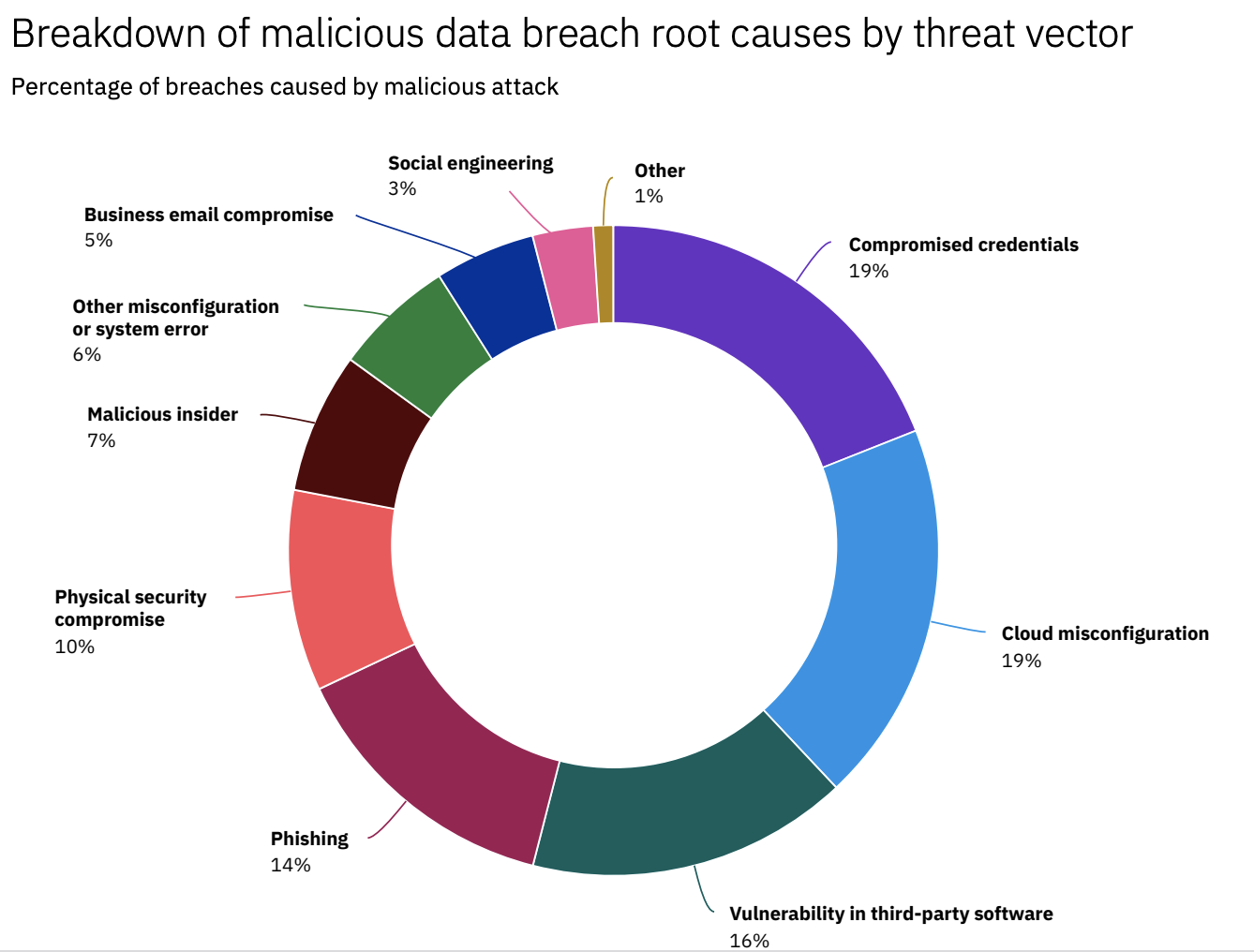 Source: Cost of Data Breach Report, IBM Security
Source: Cost of Data Breach Report, IBM Security
The three-pillar approach to information security
Confidentiality, integrity, and availability are three fundamental principles that guide the development and implementation of data security policies. Also known as the CIA triad, this framework helps organizations to protect against threats like data leaks, breaches, malware attacks, phishing, and others.- Confidentiality refers to the fact that sensitive information should be available only to authorized persons and should not be compromised;
- Integrity means that data should not be tampered with and should remain consistent, accurate, and trustworthy throughout its entire lifecycle.
- Availability involves keeping information readily available to authorized parties when it is needed.
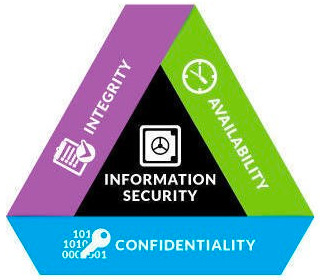 The CIA triad forms the basis for developing appropriate security policies and procedures to safeguard company’s data. Let’s dive deeper to see what security controls and solutions organizations can implement to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of business data.
The CIA triad forms the basis for developing appropriate security policies and procedures to safeguard company’s data. Let’s dive deeper to see what security controls and solutions organizations can implement to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of business data.
1. Identity and access management
Compromised credentials and mismanaged access controls present significant security threats and expose confidential business data that can be stolen or abused both by internal and external actors. To ensure information confidentiality, it is crucial to control who has access to it. To that end, organizations must implement robust identity and access management (IAM) policies that can include the following:- Single sign-on (SSO) that allows users to sign in using one set of credentials to multiple applications and systems, reducing friction and improving productivity;
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) that requires users to present at least two independent proofs of identity like a password and a temporary code sent to a phone;
- Role-based access control (RBAC) that means assigning privileges and permissions to users based on their role within the organization.
2. Data Encryption
Encrypting sensitive data is another method aimed to ensure confidentiality. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute for IBM, encryption has the greatest impact, reducing data breach costs by an average of $360,000. Best security practices include encrypting data both when it moves (in transit) and when it resides in a storage system (at rest). Essentially, there are two methods of encryption — symmetric encryption where data is encrypted and decrypted using a single private key and asymmetric encryption, where a combination of public and private keys is used. Today, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is considered to be the gold standard for data encryption. Businesses should also consider implementing full-disk encryption with tools like BitLocker to secure their remote system fleets.3. Data backups
As we have discussed earlier, data integrity is one of the cornerstones of information security. In addition to encryption, a smart data backup plan also helps to ensure data integrity and protect against permanent data loss, ransomware or malware. In practice, a robust data backup strategy includes the following steps:- Identifying what data needs to be backed up, as well as the frequency of backups;
- Choosing a storage option (disk-based, cloud-based, or a combination of those options);
- Establishing a recovery point objective (RPO) to define the maximum amount of data that can be lost without impacting operations;
- Establishing a recovery time objective (RTO) to set a timeframe a business has to access data backups and resume operations before suffering intolerable consequences;
- Testing backups to ensure all your critical data is fully preserved.
4. BYOD policy
With the remote and hybrid workplace model thriving, workers continue to use their personal laptops and mobile phones. CIRA Cyber Security report says that 50% of hybrid workforce claim they occasionally use personal devices for work purposes. If this access to corporate resources is left unmanaged and unsupervised, it can put business data at risk of theft of corruption. The practice of using personal devices for work-related activities is called BYOD (Bring Your Own Device). In order to successfully and securely embrace BYOD, companies need to follow best strategies that include strong passwords, secure network connectivity, segregation of personal and corporate data, and more. Personal devices can also be lost or stolen, and your IT department should have an action plan in place like device locking and remote wiping to ensure sensitive business data will not fall into the wrong hands.5. Employee education
According to the Global Risks Report prepared by the World Economic Forum, 95% of cybersecurity threats are traced back to human error. And while human error can have a broad definition, these numbers indicate that employees are often the weakest link in the security toolchain and can easily become the target for bad actors. Social engineering techniques used by these attackers are becoming increasingly complex and sophisticated. From phishing scams to malware to baiting and watering, cyber criminals often use emotional manipulation and trickery to gain access to a network or data.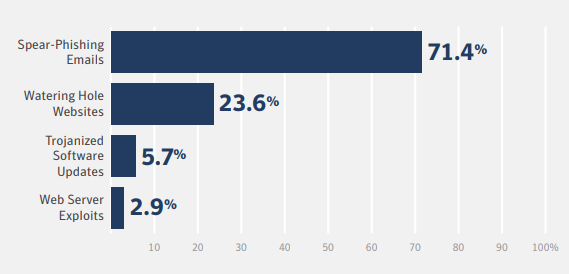
Source: Compass Security
The best defense against these attacks is to promote the culture of awareness and invest in employee training. When employees are aware of the dangers of social engineering, they are less likely to fall victim to them. Given that these attacks are evolving, employee security trainings must be conducted on a regular basis to make sure their knowledge is fresh and up-to-date.6. Proactive risk assessment
When it comes to cybersecurity, a proactive approach is always better than reactive, and a part of it is a regular risk assessment. The primary purpose of a cyber risk assessment is to evaluate an entire IT infrastructure in order to detect potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities. A risk assessment also aims to discover the most valuable data for business and what happens in case of a data breach. Risk security assessments help business leaders see blind spots, apply fixes, and patch security vulnerabilities. The findings also support a better decision-making process and help develop an effective risk mitigation plan to protect business data.Have you covered all your bases?
Ensuring data security is a complex and challenging endeavor. From implementing robust identity and access controls to end-to-end data encryption to a resilient data backup strategy, data security involves many information technologies and best practices. Companies that don’t have a security professional on their team, should consider engaging security experts to stay on top of any threats and improve security posture.Related Articles

Consequences of a Data Breach in Healthcare: Lessons from the CPAP Medical Cyberattack
In December 2024, a cyberattack hit CPAP Medical Supplies and Services, a Florida-based company that supplies sleep apnea equipment. This attack exposed the private information of over 90,000 patients, including U.S. military members and their families. This incident, which went undetected for more than six months, is not simply a one-off event. It serves as…Learn More
Machine Learning for Fraud Detection: Evolving Strategies for a Digital World
Digital banking and e-commerce have changed how we transact, creating new opportunities for criminals. Businesses lose an estimated $5 trillion to fraud each year. The sheer number of fast-paced digital transactions is too much for older fraud detection methods. These traditional tools are often too slow and inflexible to stop today's automated threats. This new…Learn More
A Detailed Guide to Cloud Vulnerability Management
With our heavy reliance on the cloud today, organizations must be aware that its convenience may come at a cost if not properly managed. Forrester’s analysis highlights a significant cybersecurity crisis, revealing that only in 2022, the year’s 35 most significant data breaches compromised over 1.2 billion customer records. These breaches had far-reaching consequences, harming brand…Learn More
Navigating the Pros and Cons of Staff Augmentation Teams and Feature-based Teams in the Tech Landscape
Are you a business owner grappling with decisions about the structure of your development team? In navigating the technological landscape, two recognized models—staff augmentation and feature-based teams—stand out as potential drivers for success. This article will observe the key factors influencing the preference for these team structures, shedding light on the critical choices companies face,…Learn More

