As the healthcare landscape rapidly evolves, the traditional saying “There’s no place like home” is being transformed through the lens of telehealth, personal emergency response systems (PERS), and remote monitoring technologies.
These innovations are steering the healthcare system toward a model that is more accessible, cost-effective, and outcome-oriented, especially for seniors.
Industry leaders are now sharing insights on how technology is shifting care from the hospital to the home, leveraging technological advancements to transform at-home healthcare.
In this article, we will define telehealth by outlining the differences between telehealth, telemedicine, and remote monitoring, reveal its benefits and challenges, and demonstrate five use cases.
Telehealth refers to the usage of digital technologies to access and manage health care services remotely.
This includes everything from video consultations and remote monitoring of vital signs to the digital transmission of medical records.
It represents a comprehensive approach to delivering healthcare services and managing patient care through technological means.
Although often used interchangeably, telehealth, telemedicine, and remote patient monitoring each hold their distinct niche in the digital healthcare ecosystem.
Telehealth is the overarching concept, covering a wide range of technologies and services designed to deliver care from a distance.
Meanwhile, telemedicine focuses on the clinical side, enabling doctors and other healthcare professionals to consult with patients remotely.
Remote patient monitoring, a subset of telemedicine, involves continuously or regularly tracking patients’ health metrics. This is achieved through wireless devices that measure and transmit information about various health indicators such as weight, blood pressure, sugar levels, and heart rate.
The definition and the main discrepancies of telehealth, telemedicine and remote patient monitoring are demonstrated in the table below.
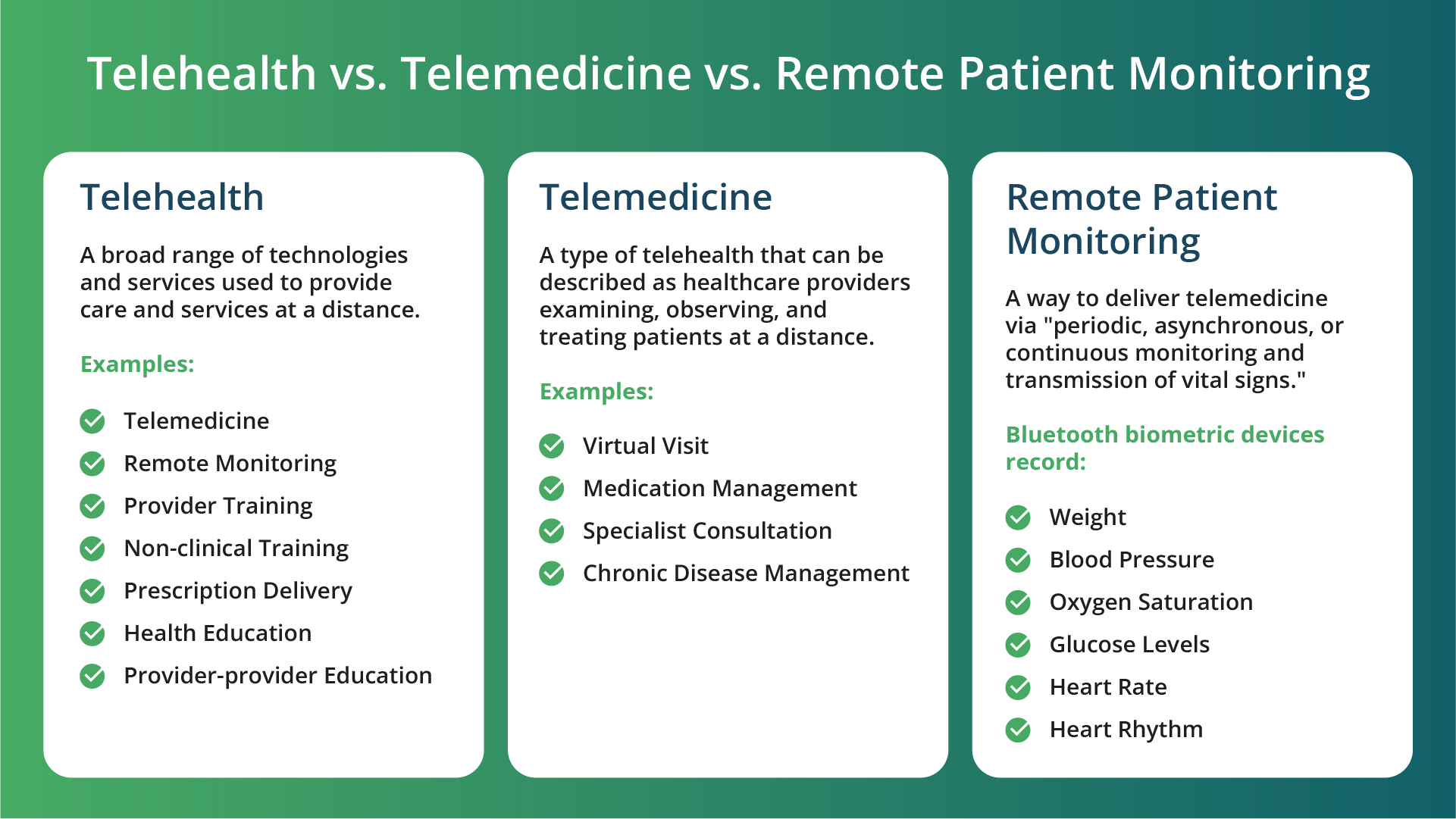 Telehealth vs Telemedicine vs Remote Patient Monitoring
Telehealth vs Telemedicine vs Remote Patient Monitoring
The move towards at-home healthcare is propelled by the need to reduce the pressures of traditional healthcare settings.
It offers a way to deliver care that is both accessible and effective within the comfort of one’s home, especially for seniors. Below are the key benefits of telehealth that make that shift possible.
Patients in remote areas can access specialist care and regular healthcare services without the need to travel.
Telehealth offers a way to receive care while minimizing exposure to infectious diseases like COVID-19.
Patients can receive care without disrupting their daily routines, eliminating travel time and costs.
Telehealth can improve communication among healthcare team members and with patients, leading to better-coordinated care and health outcomes.
Telehealth is incredibly versatile, offering various types of care:
For follow-ups and regular health assessments, eliminating the need for physical travel.
Therapy and counseling sessions can be conducted virtually, providing essential mental health support.
Patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease can receive ongoing monitoring and management advice.
Access to specialists who might not be available locally, providing expert care regardless of geographical limitations.
Telehealth has been utilized in various innovative ways across the healthcare landscape, providing care and support to patients in diverse scenarios.
Here are five real-life examples of telehealth applications:
Patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease utilize telehealth platforms for regular monitoring and management.
For example, they can transmit blood sugar levels or blood pressure readings to their healthcare provider for review, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment.
Telehealth has become a critical tool for providing mental health services, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Patients can engage in therapy sessions with psychologists or psychiatrists through video calls, ensuring continuity of care while maintaining social distancing.
After surgery, patients can use telehealth services for follow-up visits. This allows surgeons or physicians to assess healing, address any concerns, and provide further instructions for care without the need for the patient to travel to the clinic or hospital.
Patients with skin conditions can benefit from telehealth by sending photos of their skin issues to dermatologists. The dermatologist can then evaluate the images, diagnose the condition, and prescribe treatment, all without an in-person visit.
Telehealth platforms enable physical therapists to guide patients through exercises and rehabilitation routines remotely. Patients can set up their device in a way that allows the therapist to observe their movements and provide real-time feedback and modifications.
These examples illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of telehealth in enhancing access to care, improving patient outcomes, and making healthcare more convenient for both patients and providers.
As technology continues to advance, the scope and impact of telehealth are expected to grow, further transforming the healthcare delivery model.
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the value of telehealth, showcasing its ability to maintain continuity of care while adhering to social distancing measures.
A comprehensive study involving 36 million people of working age covered by private insurance revealed that the use of telemedicine surged by 766% in the initial three months of the pandemic. Telehealth has shown promise in managing chronic conditions, providing primary care, and offering access to specialists. Consistent with findings from Doximity, an online medical networking platform that includes 1.8 million doctors (roughly 80% of the physician workforce in the US) in its membership, analyses using private insurance claims data estimate that around 20% of all healthcare visits in the US during 2020 were carried out via telemedicine.
However, currently, despite its potential, telehealth faces challenges, including technological barriers for some communities, insurance reimbursement complexities, and the risk of care fragmentation.
Hopefully, ongoing advancements and policy changes will continue to address these issues, broadening telehealth’s accessibility and effectiveness.
The journey of telehealth is just beginning, with the promise of reshaping the healthcare landscape to better meet the needs of all patients, regardless of where they live.
Telehealth represents a significant leap towards a more inclusive healthcare system, where the barriers of distance, time, and accessibility are overcome through innovation.
As we embrace the transformative power of telehealth, Kanda Software stands at the forefront, ready to support your healthcare company’s digital journey. With our expertise in custom software development and deep understanding of the healthcare industry’s unique needs, we can help you navigate the complexities of digital transformation. Let Kanda be your partner in leveraging telehealth technologies to enhance patient care, improve outcomes, and drive efficiency.
Reach out to us to explore how we can tailor our solutions to meet your specific needs and make the future of healthcare accessible today.