
April 23, 2024
General
Addressing Key Scalability Challenges in Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture is a structural approach to application development in which components are divided into small and independent blocks — services. Each of these services performs specific functionality and operates as a separate process.
As the application and its services grow, there is an increasing need for scaling. At this stage, developers start facing various challenges. These challenges may be related to managing and supporting the entire infrastructure, configuring the interaction of microservices, monitoring, or other important aspects of the scaling process.
In this article, we will define the key characteristics of microservices, observe the challenges that may appear while scaling, and provide best practices for addressing these challenges.
 Addressing Key Scalability Challenges[/caption]
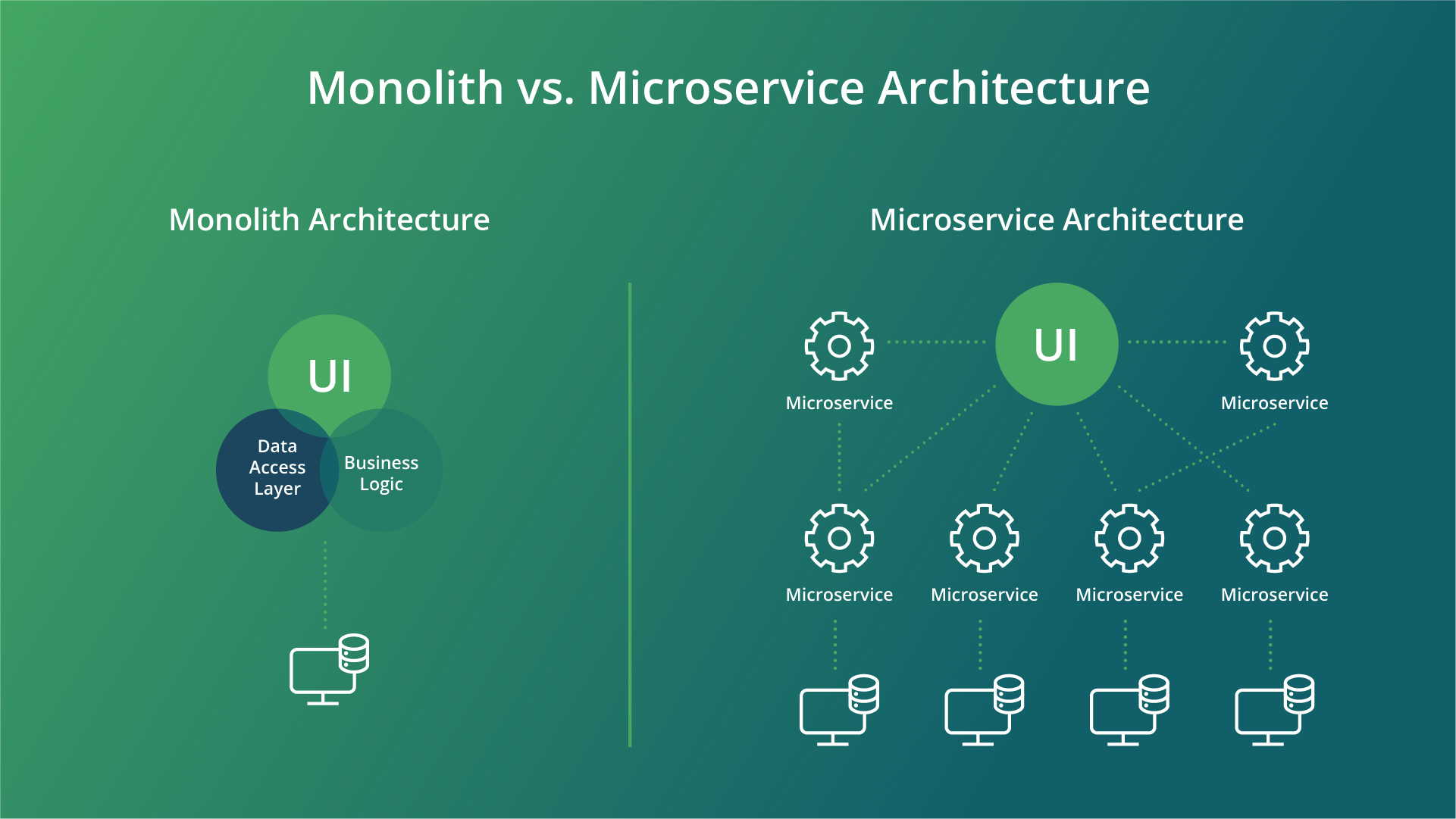
Above is a visual representation of monolith versus microservice architecture. To further elaborate on that, let’s look at eight distinctive features of microservices.
Addressing Key Scalability Challenges[/caption]
Above is a visual representation of monolith versus microservice architecture. To further elaborate on that, let’s look at eight distinctive features of microservices.
What are microservices?
Microservices are an architectural pattern in software development that consist of loosely coupled services communicating with each other through lightweight protocols. The essence of microservices is best understood by comparing or even contrasting them with a large application, a monolith. [caption id="attachment_3339" align="alignnone" width="1921"] Addressing Key Scalability Challenges[/caption]
Above is a visual representation of monolith versus microservice architecture. To further elaborate on that, let’s look at eight distinctive features of microservices.
Addressing Key Scalability Challenges[/caption]
Above is a visual representation of monolith versus microservice architecture. To further elaborate on that, let’s look at eight distinctive features of microservices.
-
Small size
-
Independence
-
Built around business need and bounded context
-
Interaction through smart endpoints and dumb pipes
-
Design for failure
-
Minimized centralization
-
Automation in development and maintenance
-
Iterative evolution
Microservices scalability: the key challenge
Scaling a monolithic application is relatively simple: you just add more resources as the volume of transactions grows. A load balancer helps distribute the load across multiple identical servers, which typically host the entire application. However, with a microservices architecture, each service can be scaled independently. In contrast, even if you've only modified one part of a monolithic application, you may still need to scale the entire application. In response to increased load, you can deploy additional instances of the application to distribute the load evenly. Scaling a microservices-based application, however, is more complex and requires a different approach than scaling a monolith. A microservices-based application comprises various services and components. To scale it, you can either scale the entire application simultaneously or identify and scale specific components and services individually.How to address microservice scalability challenges: crucial steps
Below we will reveal best practices for developers to address challenges while trying to scale microservice-based applications.Step 1. Coordination
As the number of microservices grows, so does the complexity of managing them. In this context, coordination of services within a microservices architecture is crucial. It involves managing communication and interaction among individual components across a distributed system. Three critical aspects of service coordination essential for scalability are provided below.- Service discovery
- Load balancing
- Inter-service communication
- HTTP/REST API
- Message brokers
- gRPC
Step 2. Data consistency
Ensuring data consistency becomes a complex task in a distributed environment where each microservice updates its data independently. In traditional monolithic architecture, transactions are easily managed. However, in a microservices architecture where each microservice may have its own database, executing distributed transactions becomes challenging. Using ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) transactions is not entirely suitable for microservices architecture, as this approach can lead to coordination complexity, performance and flexibility limitations, and increased database load when scaling. Below are common approaches that can help ensure data consistency when scaling microservices:- Saga pattern
- CQRS
Step 3. Performance improvement
When scaling microservices and handling a large number of requests, performance issues may arise. Below, we'll list a series of actions to help improve performance.- Data caching
- Asynchronous processing
- Horizontal scaling
- Vertical scaling
- Monitoring and optimization
Step 4. Choosing the right infrastructure
Selecting the appropriate infrastructure significantly influences the scalability of microservices, as it provides essential resources and deployment tools. The choice of available tools depends entirely on your project's requirements and the functionality of its microservices. Consider the following aspects when choosing infrastructure:- Containerization and orchestration
- Cloud platforms
- Cost evaluation
- Long-term scalability
Step 5. Monitoring and observability
Monitoring and observability play a crucial role in the successful operation of microservices architecture. They allow you to identify issues, track performance, analyze data, and take measures to optimize the system. Below are the main aspects and monitoring tools worth paying attention to.- Request tracing
- Logging
- Metric monitoring
- Event management and alerting
Step 6. Microservices resilience
In microservices architecture, where each service operates independently of others, it's important to implement mechanisms that ensure stable and reliable system operation even in case of failures and errors in individual services. This is especially relevant when it comes to microservices scaling, as the process becomes more complicated with a significant increase in the number of services. Below are some aspects and tools that will help you establish microservices resilience.- Fault tolerance
- Fault detection and recovery
- Retry mechanisms
Step 7. Security and access control
As an application grows and the number of its microservices increases, it becomes more vulnerable to security breaches. It's important to understand that implementing special mechanisms and methods can significantly enhance the security of the project as it scales. Here are some examples:- Authentication and authorization
- Data protection
-
- TLS/SSL — TLS (Transport Layer Security) or its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encrypt data during transmission between the client and the server.
- API Gateway — can provide client authentication and authorization before accessing microservices, control access to various API endpoints, and provide data encryption mechanisms.
- Security audits and testing
Conclusion
In this article, we have outlined a comprehensive guide to scaling microservices, including potential challenges that developers may encounter and tools to address them. Proper scaling ensures the stable operation and high performance of the entire system. Kanda Software has assisted a wide range of partners and customers in achieving their scalability goals. With the help of our experts, your company will be able to adhere to the best practices in microservice scaling, guaranteeing user satisfaction, and staying ahead of competitors. Are you ready to tap into the limitless scalability potential? Talk to us today!Related Articles

Custom AI Development vs Off-the-Shelf Solutions: What Delivers Better ROI?
Key Takeaways Custom AI development costs more upfront but delivers stronger long-term ROI, especially for core business functions. Off-the-shelf tools get you started fast, but subscription costs scale quickly, and vendor lock-in is a real risk. Over 80% of AI projects fail, and the most common reason isn’t the technology, it’s misalignment between the solution…Learn More
Low-Code, No-Code, or Custom Build? How Enterprises Should Actually Decide
Key Takeaways Low-code accelerates app development for professional developers; no-code empowers non-technical users to build on their own. Custom development costs more upfront but offers full control over security, scalability, and integration. Hidden costs like vendor lock-in, licensing at scale, and security gaps can erode the savings platforms promise. Most successful enterprises use a hybrid…Learn More
Why Using Edge AI for Real-Time Analytics Is Your Next Best Decision
Key Takeaways: Edge AI processes data locally in 1–10 ms, compared to 50–200 ms with cloud-based analytics, making it critical for time-sensitive operations. Organizations can cut data transmission costs by up to 43% and reduce cloud-bound traffic by over 90% by filtering data at the edge. Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities…Learn More
Why Human-in-the-Loop AI Is Necessary in the Age of Automation
AI is spreading through businesses much faster than most people anticipated. Data from a Fullview report shows that 78% of organizations now utilize artificial intelligence in at least one part of their operations, which is a significant jump from 55% back in 2023. At the same time, 71% of these companies are regularly using generative AI…Learn More

