
May 09, 2024
dotGeneral
Leveraging OLAP for Advanced Data Analysis
Although less frequently used compared to SQL (relational) and NoSQL (non-relational) data stores, OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) systems play a crucial role for companies managing analytical systems that handle enormous volumes of data—ranging into terabytes and petabytes.
In this article, we will explain the architecture of OLAP, observe its specific types, discuss their differences, and illustrate practical business use cases and future perspectives.
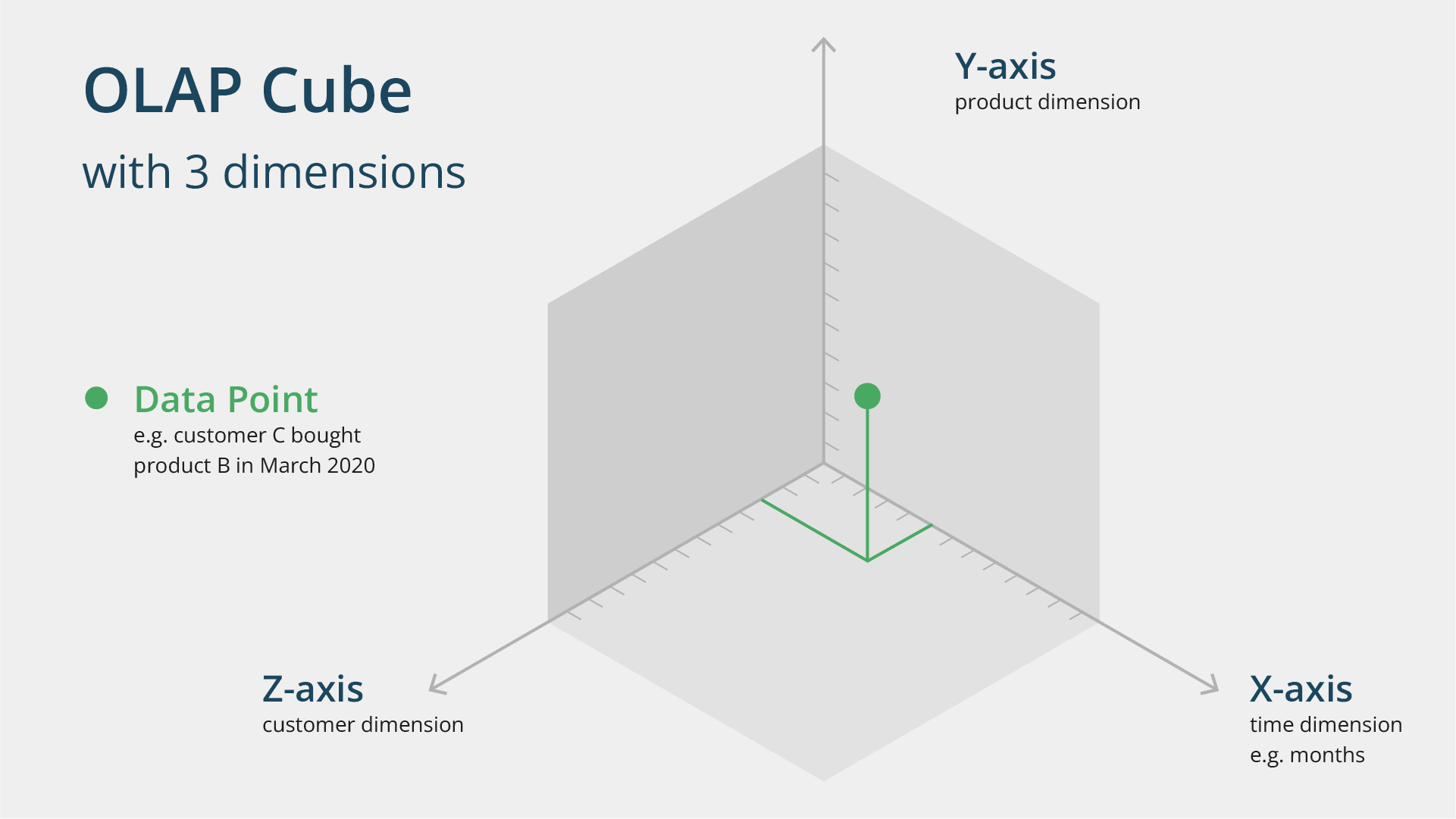 This example can be represented in a simple OLAP cube with three metrics. It can be further complicated by adding new metrics, such as property location and city district.
OLAP cubes are used to obtain data slices based on their dimensions. This allows analysts to access information from a single source without manually gathering data from disparate tables.
These data slices across different metrics are automatically generated during data preprocessing, speeding up storage query execution.
This example can be represented in a simple OLAP cube with three metrics. It can be further complicated by adding new metrics, such as property location and city district.
OLAP cubes are used to obtain data slices based on their dimensions. This allows analysts to access information from a single source without manually gathering data from disparate tables.
These data slices across different metrics are automatically generated during data preprocessing, speeding up storage query execution.
What is OLAP technology?
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is a powerful software tool that businesses use to analyze data from different angles. Companies gather data from various sources such as websites, applications, and internal systems, storing details about products, sales, and customer behavior. OLAP combines and categorizes this data to provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making. In simpler terms, it allows analysts to extract specific data sets for analysis in real-time. Let's break down how OLAP works in practice. Imagine a real estate agency needs to assess sales volumes and profitability to identify the most lucrative deals of the past year. This analysis helps them understand the factors influencing property values and the company's profitability, enabling them to optimize their operations. Manually extracting data is time-consuming, especially when dealing with different data sources for transactions and financial indicators. Analysts must manually extract the necessary data and identify relationships between them. OLAP systems automate this process and can work with different data sources containing various types of data, consolidating them based on specified criteria. But that's not all—after extracting the data, it can be visualized for reporting or detecting relationships between metrics.What are OLAP cubes?
In OLAP systems, data is stored either in relational databases or as specialized multidimensional OLAP cubes. The raw data used to build these cubes can be sourced from ordinary databases. An OLAP cube is a multidimensional array of data, with each facet containing information related to a specific attribute. Let's illustrate this using a real estate agency example. The company might store transaction data in a standard table with real estate agents’ names and the number of contracts they've closed. This results in a familiar rows-and-columns format. But what if we want to examine how each realtor's transactions are distributed throughout the months of the year? We can add a third dimension to the structure. This example can be represented in a simple OLAP cube with three metrics. It can be further complicated by adding new metrics, such as property location and city district.
OLAP cubes are used to obtain data slices based on their dimensions. This allows analysts to access information from a single source without manually gathering data from disparate tables.
These data slices across different metrics are automatically generated during data preprocessing, speeding up storage query execution.
This example can be represented in a simple OLAP cube with three metrics. It can be further complicated by adding new metrics, such as property location and city district.
OLAP cubes are used to obtain data slices based on their dimensions. This allows analysts to access information from a single source without manually gathering data from disparate tables.
These data slices across different metrics are automatically generated during data preprocessing, speeding up storage query execution.
Advantages of OLAP
The popularity of OLAP technology stems from its unique features.-
Unlimited data access
-
Centralized data storage
-
High-speed data retrieval
-
Customizable level of detail
Types of OLAP Systems
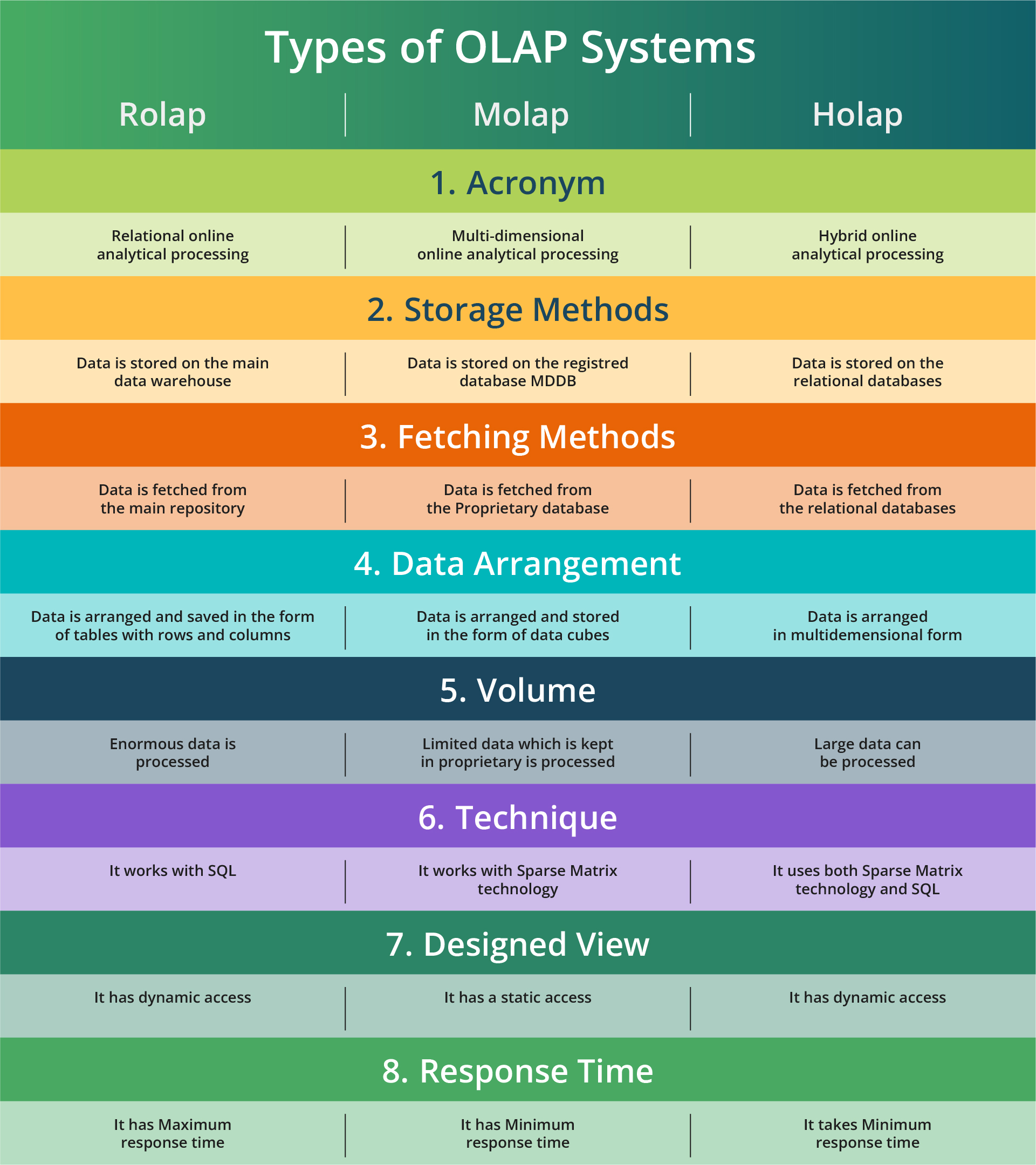
OLAP systems use one of three data storage approaches: MOLAP, ROLAP, or HOLAP. Let's explore each of them.-
MOLAP (Multidimensional OLAP)
-
ROLAP (Relational OLAP)
-
HOLAP (Hybrid OLAP)

Where OLAP is used: 3 use cases
The concept of multidimensional analysis and OLAP technology has numerous applications in business, assisting companies with organizing and analyzing large volumes of data. Let's explore its use cases across different industries.Use case 1. Sales and marketing
In sales and marketing, multidimensional analysis allows companies to identify the most profitable segments, considering parameters such as geography, product categories, time periods, and sales channels. OLAP systems enable in-depth analysis of sales dynamics, trend identification, and determination of key success factors. With multidimensional analysis, companies can create detailed customer segments based on preferences, purchase history, behavioral data, and demographics. This information helps in crafting personalized offers and optimizing targeted advertising strategies and marketing campaigns.Use case 2. Logistics and manufacturing
Manufacturing companies use OLAP for analyzing data across all stages of the production process, from raw material procurement to finished goods. The system may analyze production line efficiency, inventory management, or energy consumption. Multidimensional analysis is applied to optimize inventory management, enabling companies to visualize demand dynamics, production efficiency, and inventory levels. This helps in avoiding excessive warehouse costs and minimizing the risk of product shortages. Monitoring production processes through multidimensional models identifies production bottlenecks, improves efficiency, and reduces costs. The result is optimized production processes, reduced energy and raw material costs, and improved product quality.Use case 3. Telecommunications
Telecommunications companies use OLAP for analyzing service consumption data, traffic management, and service quality assessment. Network service monitoring involves analyzing the quality of provided telecommunications services, network load analysis, and preventing potential failures. Multidimensional analysis also aids in understanding consumer behavior by providing insights into customer preferences, activity levels, and service usage predictions. Notably, the sheer volume of data requires real-time analysis to swiftly respond to changes.Challenges of typical OLAP architecture systems and potential solutions
Despite the wide range of applications and the diversity of the usage, OLAP technologies have several drawbacks. Let's take a closer look at the shortcomings of OLAP architecture.-
Complex implementation
-
Complex data integration
-
Overlooking optimization
-
Data security risks
-
Cost and infrastructure
The future of OLAP technologies
The future development of OLAP technologies aims to enhance functionality, improve user interaction, and adapt to modern business requirements. Below are some of the key perspectives:-
Integration with AI
-
Advancements in cloud technologies
-
Augmented and virtual reality
-
Blockchain integration
-
Expanded data visualization capabilities
Key takeaways
This article provides an overview of the current state of OLAP and looks ahead to its future, emphasizing that this technology will continue to evolve, becoming more efficient and adaptable to the dynamics of the modern business landscape. However, successful implementation and utilization of OLAP requires not only technical expertise but also a deep understanding of specific business processes. At Kanda, our expert team is dedicated to addressing daily technological challenges. If your company seeks to process large volumes of information for insightful solutions and informed decision-making, we're here to collaborate and build meaningful solutions together. Get in touch with our experts and let's harness the power of innovation to drive business success, together.Related Articles

Comprehensive AI Security Strategies for Modern Enterprises
Over the past few years, AI has gone from a nice-to-have to a must-have across enterprise operations. From automated customer service to predictive analytics, AI technologies now handle sensitive data like never before. A Kiteworks report shows that over 80% of enterprises now use AI systems that access their most critical business information. This adoption…Learn Morearrow-right
Building Trust in AI Agents Through Greater Explainability
We’re watching companies leap from simple automation to an entirely new economy driven by self-governing AI agents. According to Gartner, by 2028 nearly a third of business software will have agentic AI built in, and these agents will be making at least 15% of everyday work decisions on their own. While that can significantly streamline…Learn Morearrow-right
Machine Learning for Fraud Detection: Evolving Strategies for a Digital World
Digital banking and e-commerce have changed how we transact, creating new opportunities for criminals. Businesses lose an estimated $5 trillion to fraud each year. The sheer number of fast-paced digital transactions is too much for older fraud detection methods. These traditional tools are often too slow and inflexible to stop today's automated threats. This new…Learn Morearrow-right
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC): Helping You Understand Simply and Completely
Software development is a complex and challenging process, requiring more than just writing code. It requires careful planning, problem solving, collaboration across different teams and stakeholders throughout the period of development. Any small error can impact the entire project, but Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provides the much needed support to overcome the complexities of…Learn Morearrow-right

